AI is creating a shift in the way we work, create, and decide. But recently these two terms keep on popping up: agentic AI and generative AI.
They can sound quite similar, but they do quite different jobs.
Let me break down what they are, how they differ and how they actually work in the real world.
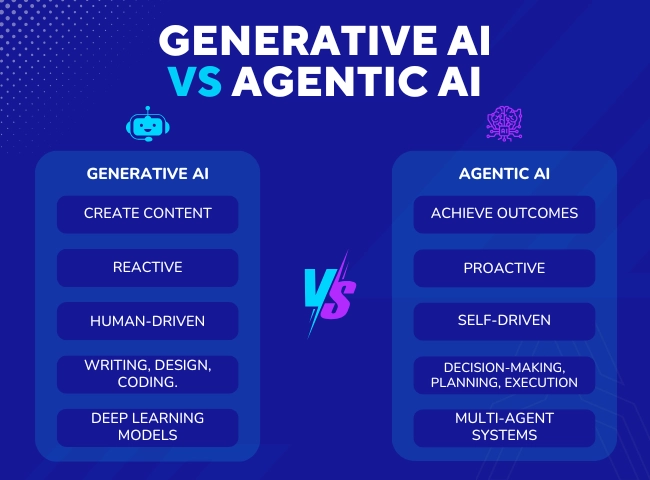
What is Generative AI
Generative AI can build something from data, like a writer, designer or coder who never sleeps.
When you ask it to summarize a report or write an ad it draws from patterns it learned during training.
Core features:
This is why prompt engineering matters. The difference is not subtle.
- Content creation: Writes text, generates images, and even produces music or code.
- Data analysis: Spots patterns across massive datasets.
- Adaptability: Improves responses when given feedback.
- Personalization: Customizes content for each user or audience.
Agentic AI Explained
Agentic AI takes initiative. It can plan, reason and act based on whatever it learns.
It’s built on technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and reinforcement learning.
This isn’t paranoia. It’s survival.
Key traits:
- Decision-making: Assesses context and selects the best next action.
- Problem-solving: Follows a four-step loop—perceive, reason, act, learn.
- Autonomy: Works on its own with limited supervision.
- Interactivity: Adjusts in real time to live data.
- Planning: Handles multi-step tasks toward a goal.
Example:
A digital assistant built on agentic AI might receive a target, say, “schedule sales calls with all qualified leads this week.” It could check the CRM, send emails, confirm meetings, and update records, without human nudges.
Here’s a clean comparison:
How They Work Together
In most modern tools, agentic AI and generative AI combine.
A system might plan tasks like an agent, then call a generative model to create text or design content.
Example flow:
Agentic AI decides: “We need to send a follow-up email to 20 leads.”
It gathers data and prompts the generative model: “Write personalized follow-up emails for each lead.”
The generative model drafts the messages.
The agent reviews, edits, and sends them automatically.
Common Use Cases
Generative AI in Action
- SEO content: Drafts blogs and landing pages optimized for ranking.
- Marketing copy: Creates ad headlines, captions, and emails at scale.
- Product design: Suggests design ideas from trend data.
- Customer support: Generates responses for FAQs and support chats.
Agentic AI in Action
- Customer service: Handles conversations, detects intent, and resolves issues.
- Healthcare: Tracks patient data and alerts doctors when action is needed.
- Workflow automation: Adjusts schedules, updates systems, reorders supplies.
- Finance: Monitors market data, reallocates portfolios in real time.
The Trendline: Where It’s Heading
Generative AI Trends
- Augmented apps: Tools with built-in writing or design support.
- Synthetic data: AI-generated data for safer model training.
- Deepfakes: Realistic but risky use of AI in media.
- Personalized content: Real-time tailoring for each user.
Agentic AI Trends
- Finance: Real-time trading decisions and risk control.
- Robotics: Smarter warehouse and delivery bots.
- Urban planning: AI systems that optimize city traffic.
- Human resources: Automated employee support and scheduling.
Takeaway
Generative AI gave us tools that create at speed, serving as a powerful creative assistant. Agentic AI adds the power to think and act, moving beyond simple output generation to complex, autonomous problem-solving.
Agentic AI further expands into specialized systems, where the right automation (workflow or agent) is chosen to tackle specific, complex tasks.
If your goal is creation, use generative AI. If your goal is action, use agentic AI. And if you want real business value, combine both.